The Jewish National Fund, established more than 100 years ago, is perhaps the most venerable of the international Zionist organizations. Its recent honorary patrons have included prime ministers, and it advises UN forums on forestry and conservation issues.
It is also recognized as a charity in dozens of western states. Generations of Jewish families, and others, have contributed to its fundraising programs, learning as children to drop saved pennies into its trademark blue boxes to help plant a tree.
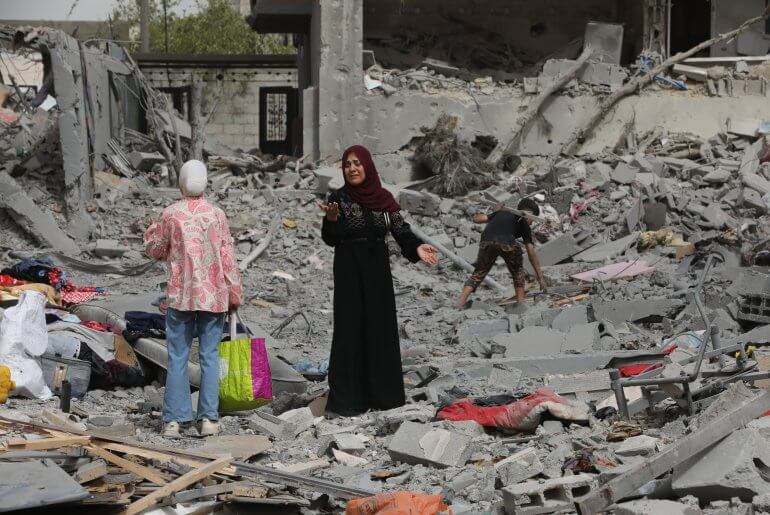
And yet its work over many decades has been driven by one main goal: to evict Palestinians from their homeland.
The JNF is a thriving relic of Europe’s colonial past, even if today it wears the garb of an environmental charity. As recent events show, ethnic cleansing is still what it excels at.
The organization’s mission began before the state of Israel was even born. Under British protection, the JNF bought up tracts of fertile land in what was then historic Palestine. It typically used force to dispossess Palestinian sharecroppers whose families had worked the land for centuries.
But the JNF’s expulsion activities did not end in 1948, when Israel was established through a bloody war on the ruins of the Palestinians’ homeland – an event Palestinians call the Nakba, or catastrophe.
Israel hurriedly demolished more than 500 cleansed Palestinian villages, and the JNF was entrusted with the job of preventing some 750,000 refugees from returning. It did so by planting forests over both the ruined homes, making it impossible to rebuild them, and village lands to stop them being farmed.
These plantations were how the JNF earned its international reputation. Its forestry operations were lauded for stopping soil erosion, reclaiming land and now tackling the climate crisis.
But even this expertise – gained through enforcing war crimes – was undeserved. Environmentalists say the dark canopies of trees it has planted in arid regions such as the Negev, in Israel’s south, absorb heat unlike the unforested, light-colored soil. Short of water, the slow-growing trees capture little carbon. Native species of brush and animals, meanwhile, have been harmed.
These pine forests – the JNF has planted some 250 million trees – have also turned into a major fire hazard. Most years hundreds of fires break out after summer droughts exacerbated by climate change.
Early on, the vulnerability of the JNF’s saplings was used as a pretext to outlaw the herding of native black goats. Recently the goats, which clear undergrowth, had to be reintroduced to prevent the fires. But the goats’ slaughter had already served its purpose, forcing Bedouin Palestinians to abandon their pastoral way of life.
Despite surviving the Nakba, thousands of Bedouin in the Negev were covertly expelled to Egypt or the West Bank in Israel’s early years.
It would be wrong, however, to imagine that the JNF’s troubling role in these evictions was of only historical interest. The charity, Israel’s largest private land owner, is actively expelling Palestinians to this day.
In recent weeks, solidarity activists have been desperately trying to prevent the eviction of a Palestinian family, the Sumarins, from their home in occupied East Jerusalem to make way for Jewish settlers.
Last month the Sumarins lost a 30-year legal battle waged by the JNF, which was secretly sold their home in the late 1980s by the Israeli state.
The family’s property was seized – in violation of international law – under a draconian 1950 piece of legislation declaring Palestinian refugees of the Nakba “absent”, so that they could not reclaim their land inside the new state of Israel.
The Israeli courts have decreed that the Absentee Property Law can be applied outside Israel’s recognized territory too, in occupied Jerusalem. In the Sumarins’ case, it appears not to matter that the family was never actually “absent”. The JNF is permitted to evict the 18 family members next month. To add insult to injury, they will have to pay damages to the JNF.
A former US board member, Seth Morrison, resigned in protest in 2011 at the JNF’s role in such evictions, accusing it of working with extreme settler groups. Last year the JNF ousted a family in similar circumstances near Bethlehem. Days later settlers moved on to the land.
Ir Amim, an Israeli human rights group focusing on Jerusalem, warned that these cases create a dangerous legal precedent if Israel carries out its promise to annex West Bank territory. It could rapidly expand the number of Palestinians classified as “absentees”.
But the JNF never lost its love of the humble tree as the most effective – and veiled – tool of ethnic cleansing. And it is once again using forests as a weapon against the fifth of Israel’s population who are Palestinian, survivors of the Nakba.
Earlier this year it unveiled its “Relocation Israel 2040” project. The plan is intended to “bring about an in-depth demographic change of an entire country” – what was once sinisterly called “Judaization”. The aim is to attract 1.5 million Jews to Israel, especially to the Negev, over the next 20 years.
As in Israel’s first years, forests will be vital to success. The JNF is preparing to plant trees on an area of 40 sq km belonging to Bedouin communities that survived earlier expulsions. Under the cover of environmentalism, many thousands of Bedouin could be deemed “trespassers”.
The Bedouin have been in legal dispute with the Israeli state for decades over ownership of their lands. This month in an interview with the Jerusalem Post newspaper, Daniel Atar, the JNF’s global head, urged Jews once again to drop money into its boxes. He warned that Jews could be dissuaded from coming to the Negev by its reputation for “agricultural crimes” – coded reference to Bedouin who have tried to hold on to their pastoral way of life.
Trees promise both to turn the semi-arid region greener and to clear “unsightly” Bedouin off their ancestral lands. Using the JNF’s original colonial language of “making the desert bloom”, Atar said his organization would make “the wilderness flourish”.
The Bedouin understand the fate likely to befall them. In a protest last month they carried banners: “No expulsions, no displacement.”
After all, Palestinians have suffered forced displacement at the JNF’s hands for more than a century, while watching it win plaudits from around the world for its work in improving the “environment”.
A version of this article first appeared in the National, Abu Dhabi.
Jonathan Cook
Jonathan Cook won the Martha Gellhorn Special Prize for Journalism. His latest books are “Israel and the Clash of Civilisations: Iraq, Iran and the Plan to Remake the Middle East” (Pluto Press) and “Disappearing Palestine: Israel’s Experiments in Human Despair” (Zed Books). His new website is jonathan-cook.net.



From a Canadian friend:
Re “Canada Park”:
Before dawn on June 6, one day after Israel launched the 1967 war,“Three villages in the fertile Latrun Valley [under Jordanian administration in accordance with the 1949 armistice agreement with Israel] that had defied capture in 1948…were totally razed by Israeli bulldozers, their residents scattered without concern for their future. Beit Nuba, Imwas [the latter believed by Christians to be where Jesus first appeared after his resurrection] and Yalu lay just across the frontier on the West Bank, about fifteen miles northwest of Jerusalem, and obstructed a direct route from Jerusalem to Tel Aviv. The [10,000 or more] residents had been ordered out…without explanation, given no chance to rescue their possessions except for what they could carry, left to wander without shelter or food or water.” They were never permitted to return. (Donald Neff, Warriors for Jerusalem: The Six Days That Changed the Middle East in 1967, Amana Books Brattleboro, Vermont, 1988, p. 290)
Even though the inhabitants put up no resistance, the three villages were demolished on the direct orders of Yitzhak Rabin, Chief of Staff of the Israeli army. Several of the villages’ elders who were unable to walk without assistance were killed by falling rubble as Israel’s bulldozers demolished their homes.
What transpired when Israel attacked, seized, ethnically cleansed and demolished the three villages is well documented in “Memory of the Cactus,” a 2008 documentary film directed by Hanna Musleh and produced by the Palestinian human rights organization, Al-Haq. Dr. Ismail Zayid, now a Canadian and a highly respected and tireless advocate for his fellow Palestinians, was born in Beit Nuba. CBC Television’s Fifth Estate produced a documentary on Canada Park featuring Dr. Zayid. (cont’d)
Here’s the JNF site: https://www.jnf.org/menu-2/our-vision
” Israel’s population cannot remain concentrated on a vulnerable coastal plain, and a vibrant north and south should be attractive new frontiers for Israeli families….”
I guess that means more settlements?
Despite their usual cries of victim, it is obvious it is the occupier, Israel, that is wiping the Palestinians off the map, and in fact drawing maps showing they don’t exist.
The US hands them the erasers.
The Jewish groups like the JNF and others who pretend they are actively working to protect Israel,
have been established to help this land thief and human rights violator, achieve their illegal nation built on stolen disputed lands. One of the reasons Israel is one of the most disliked nations in the world.
Reply to Abe Bird. (cont’d)
48% of the total land area of mandated Palestine was privately owned (‘mulk khaas’) by Palestinian Arabs. (To repeat, total Jewish privately owned land was between 6% and 7%.) About 45% of the total land area was state owned (i.e., by its citizens)* and it was comprised of Communal Property (‘mashaa’), Endowment Property, (‘waqf’), and Government Property, (‘miri’.) The British Mandate kept an extensive land registry and the UN used the registry during its early deliberations. It has in its archives 453,000 records of individual Palestinian owners defined by name, location & area. *Only 30% of the Jewish immigrants had taken out citizenship & tens of thousands were illegals.
Land ownership in all of mandated Palestine on Nov. 29, 1947: By Sub district – Acre: 87% Palestinian owned, 3% Jewish owned, 10% state owned; Safed: 68% Palestinian owned, 18% Jewish owned, 14% state owned; Haifa: 42% Palestinian owned, 35% Jewish owned, 23% state owned; Nazareth: 52% Palestinian owned, 28% Jewish owned, 20% state owned; Tiberias: 51% Palestinian owned, 38% Jewish owned, 11% state owned; Jenin: 84% Palestinian owned, less than 1% Jewish owned, 16% state owned; Beisnan: 44% Palestinian owned, 34% Jewish owned, 22% state owned; Tulkarm: 78% PalestinIan owned; 17% Jewish owned, 5% state owned; Nablus: 87% Palestinian owned, less than 1% Jewish owned, 13% state owned; Jaffa: 47% Palestinian owned, 39% Jewish owned, 14% state owned; Ramleh: 77% Palestinian owned, 14% Jewish owned, 9% state owned; Ramallah: 99% Palestinian owned, less than 1% Jewish owned, less than 1% state owned; Jerusalem (West and East): 84% Palestinian owned, 2% Jewish owned, 14% state owned; Gaza: 75% Palestinian owned, 4% Jewish owned, 21% state owned; Hebron: 96% Palestinian owned, less than 1% Jewish owned, 4% state owned; Bersheeba: 15% Palestinian owned, less than 1% Jewish owned, 85% state owned. (Village Statistics, Jerusalem: Palestine Government, 1945) (cont’d)
Reply to Abe Bird, (cont’d)
Regarding land ownership in West and East Jerusalem in 1947: The total land area of West Jerusalem (the New City) was 19,331 dunams (about 4,833 acres) of which 40 per cent was owned by Palestinian Muslims and Christians, 26.12 per cent by Jews and 13.86 per cent by others, including Christian communities. Government and municipal land made up 2.90 per cent and roads and railways 17.12 per cent.
East Jerusalem (the Old City) consisted of 800 dunams (about 200 acres) of which five dunams (just over one acre) were Jewish owned and the remaining 795 dunams were owned by Palestinian Muslims and Christians. (“Assessing Palestinian Property in the City,” by Dalia Habash and Terry Rempel, Jerusalem 1948: The Arab Neighbourhoods and their Fate in the War, 1999, pp. 184-85)